Non Permanent Birth Control | Pros & Cons
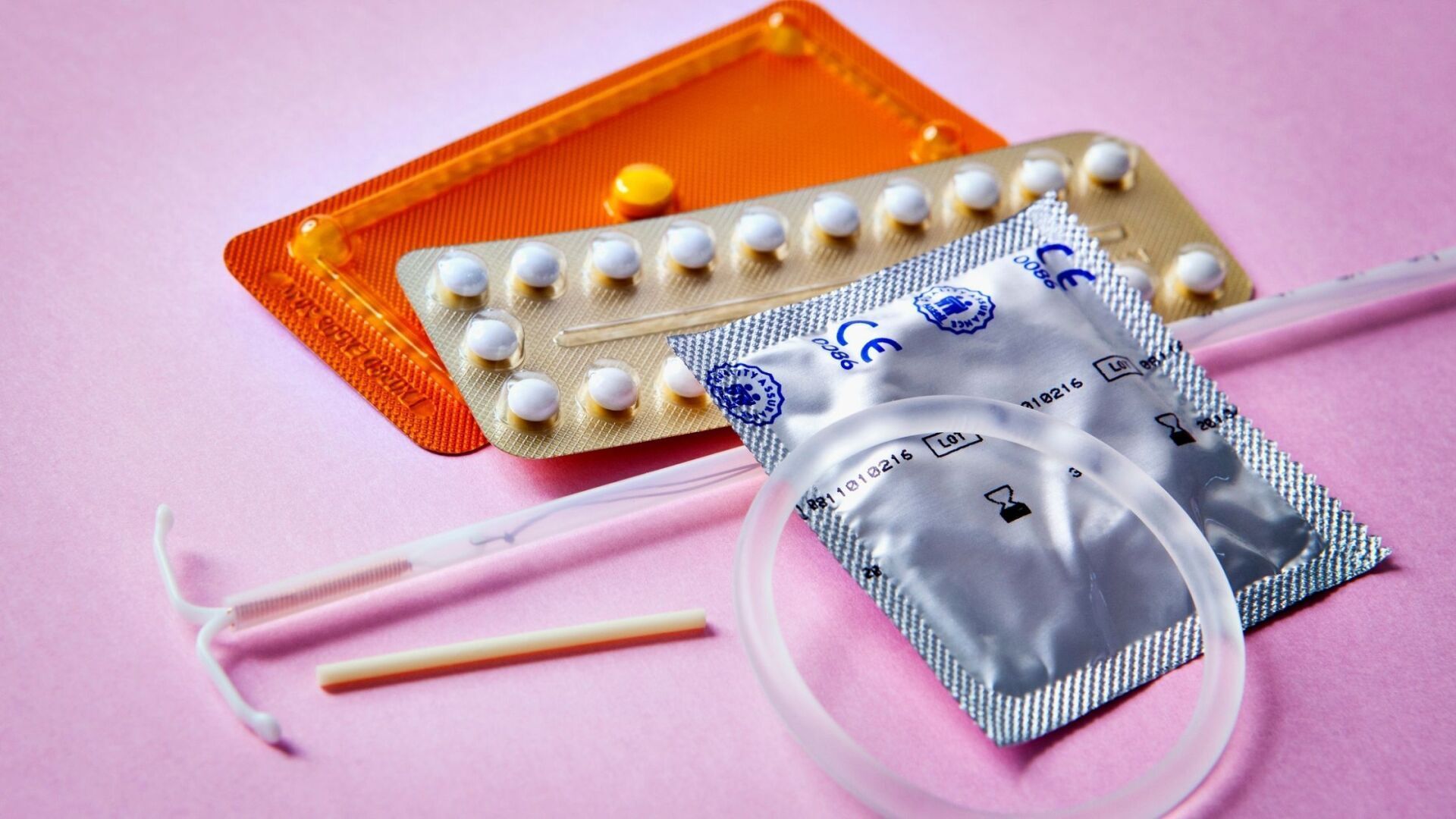
The reasons women and young women choose to use a form of birth control is as varied as women themselves. One reason is obvious, to avoid pregnancy. Hormonal birth control methods can help regulate periods, sometimes eliminating menstrual cycles (which will return when the hormonal methods are terminated), treat acne and/or help prevent ovarian cysts. The only birth control method that helps prevent sexually transmitted diseases is the condom.
Intrauterine devices or IUDs
Hormonal IUD — Mirena, Skyla and Liletta are hormonal IUDs with protection ranging from 3 years for the Skyla and Liletta to 5 years for the Mirena. These are small T shaped devices inserted into the uterus that release progestin, preventing the ovaries from releasing an egg and causing the cervical mucus to thicken so sperm can’t reach the egg. A healthcare provider inserts the IUD.
Copper IUD — The ParaGard is a small T shaped device inserted into the uterus that releases a small amount of copper into the uterus preventing the sperm from reaching and fertilizing the egg. If fertilization occurs, the IUD keeps the fertilized egg from implanting in the uterus lining. A healthcare provider inserts the copper IUD. It can provide protection for 10 years.
Pros — Due to low user error, IUDs are one of the most effective birth control methods on the market. They are also one of the most affordable methods. Many insurance plans cover IUDs at 100%.* They can be removed at any time if birth control is no longer desired. Studies suggest that hormonal IUDs not only reduce heavy menstrual bleeding by up to 90 percent after several months of use, but often cause women to stop getting their periods altogether.
Cons — Cramping is common the first 24-48 hours after an IUD is inserted. Some women may experience cramping for a few days, weeks or months as their bodies adjust. Copper IUDs do not reduce menstrual bleeding. None of the IUDs improve hormone related acne as they do not contain estrogen.
Nexplanon
This is an implantable rod which is matchstick-size, flexible rod that is put under the skin of the upper arm. The rod releases a progestin, which causes changes in the lining of the uterus and the cervical mucus to keep the sperm from joining an egg. It is effective for up to 3 years.
Pros — Due to low user error, it is one of the most effective birth control methods on the market. It is one of the most affordable methods. Many insurance plans cover the Nexplanon at 100%.* It can be removed at any time if birth control is no longer desired.
Cons — Changes in the intensity, frequency or duration of menstrual bleeding is the most common reason given for removal of Nexplanons prior to 3 years. Other undesirable side effects sited are acne, weight gain, headaches and/or breast pain.
Oral contraceptives — "The Pill"
The Pill contains the hormones estrogen and progestin. It prevents the ovaries from releasing an egg. It also causes changes in the lining of the uterus preventing the sperm from joining the egg. Many types of oral contraceptives are offered. Consult your healthcare provider to determine which is best for you.
If you have any of the below risk factors, the pill may not be the best birth control for you:
- Over 35 years of age and smoke
- Have a history of blood clots
- Have a history of breast, liver, or endometrial cancer
Pros — The Pill may make menstrual cycles more regular (or eliminate cycles with certain pills), may reduce bleeding and cramping with monthly cycles and may reduce pain with ovulation. The Pill may also help protect against ovarian and endometrial cancer, reduce the symptoms of endometriosis, reduce ovarian cysts and reduce acne. Many insurance plans cover certain oral contraceptives at 100%.*
Cons — Effectiveness of The Pill is diminished if it is not taken at the same time daily. Reported undesirable side effects include weight gain, bloating and headaches. Antibiotics may reduce the effectiveness of The Pill.
Depo-Provera
This is an injection of the hormone progestin which needs to be repeated every 3 months. The shot stops the ovaries from releasing an egg and causes changes in the cervix that keep the sperm from joining with the egg. Because the injection can cause temporary loss of bone density it should not be used more than 2 years in a row. The loss increases the longer this method is used. The bone density starts increasing after depo-provera is stopped. It may increase the risk of fracture and osteoporosis if used long- term.
Pros — Each injection provides 3 months protection against pregnancy. Many women stop having monthly cycles. It may protect against uterine cancer. Many insurance plans cover depo-provera injections prescribed as a contraceptive at 100%.*
Cons — The injection requires a visit to your providers office every 3 months. The injection may cause a decrease in bone density. Some reported side effects include weight gain, fatigue and irregular bleeding.
NuvaRing
This is a thin, flexible vaginal ring that releases the hormones progestin and estrogen. It stops the ovaries from releasing eggs and thickens the cervical mucus, preventing the sperm from joining the egg. The ring is squeezed between the thumb and index finger and inserted into the vagina. The ring is worn for 3 weeks and then removed for a week to allow a menstrual cycle. Then a new ring is inserted.
Pros — The ring is very effective if used correctly. It may make menstrual cycles more regular and may reduce bleeding and cramping with monthly cycles. It may help protect against ovarian and uterine cancer, reduce ovarian cysts and reduce acne. Many insurance plans cover NuvaRing at 100%.*
Cons —The ring needs to be inserted correctly to be effective. Reported undesirable side effects include vaginal infections and irritation, vaginal discharge, weight gain, and nausea.
*The Affordable Care Act mandates that new health insurance plans offer at least one form of each of the 18 FDA- approved methods of birth control for women without a co-payment to the patient. Some existing health insurance plans were grandfathered and not required to meet this requirement. Each insurance plan is different, you should always check with your plan to determine coverage for the method you desire.



